#include <string>#include <float.h>#include "asserts.h"#include "types.h"#include "estring.h"

Go to the source code of this file.
Classes | |
| class | safe_num< T > |
| Safely manipulate numbers without worryiung about over/underflow error. More... | |
Functions | |
| template<typename T > | |
| static const T | max_limit () |
| A small set of numeric limits routines, since gcc prior to 3.x doesn't have numeric_limits. | |
| template<typename T > | |
| static const T | min_limit () |
| Find the maximum limit for a type, equivalent to std::numeric_limits<T>.min() for systems that don't have the limits c++ header file. | |
| template<> | |
| const float | max_limit< float > () |
| Return the largest possible number that a float may hold. | |
| template<> | |
| const float | min_limit< float > () |
| Return the smallest positive number that a float may hold. | |
| template<> | |
| const double | max_limit< double > () |
| Return the largest possible number that a double may hold. | |
| template<> | |
| const double | min_limit< double > () |
| Return the smallest positive number that a double may hold. | |
| template<typename T > | |
| static const T | max_limit (const T &a_arg) |
| Return the max_limit of a variable. | |
| template<typename T > | |
| static const T | min_limit (const T &a_arg) |
| Return the min_limit of a variable. | |
| template<typename T > | |
| static const T | highest_value (void) |
| Return the maximum possible value a type may hold. | |
| template<typename T > | |
| static const T | highest_value (const T &a_arg) |
| Return the maximum possible value of a variable. | |
| template<typename T > | |
| static const T | lowest_value (void) |
| Return 0 for unsigned types, or the maximum negative value that the type may hold. | |
| template<typename T > | |
| static const T | lowest_value (const T &a_arg) |
| Return 0 for unsigned types, or the maximum negative value that a variable may hold. | |
| template<typename T > | |
| T | absolute (const T &a_num) |
| Return the absolute value of a numeric type. | |
| template<typename T > | |
| safe_num< T > | operator+ (safe_num< T > a_class1, safe_num< T > a_class2) |
| Arithmetic operator. | |
| template<typename T > | |
| safe_num< T > | operator- (safe_num< T > a_class1, safe_num< T > a_class2) |
| Arithmetic operator. | |
| template<typename T > | |
| safe_num< T > | operator* (safe_num< T > a_class1, safe_num< T > a_class2) |
| Arithmetic operator. | |
| template<typename T > | |
| safe_num< T > | operator/ (safe_num< T > a_class1, safe_num< T > a_class2) |
| Arithmetic operator. | |
| template<typename T > | |
| safe_num< T > | operator% (safe_num< T > a_class1, safe_num< T > a_class2) |
| Arithmetic operator. | |
| template<typename T > | |
| safe_num< T > & | operator++ (safe_num< T > &a_class) |
| Arithmetic operator. | |
| template<typename T > | |
| safe_num< T > | operator++ (safe_num< T > &a_class, int) |
| Arithmetic operator. | |
| template<typename T > | |
| safe_num< T > & | operator-- (safe_num< T > &a_class) |
| Arithmetic operator. | |
| template<typename T > | |
| safe_num< T > | operator-- (safe_num< T > &a_class, int) |
| Arithmetic operator. | |
| template<typename T > | |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &a_out, safe_num< T > a_class) |
| Arithmetic operator. | |
| template<typename T > | |
| std::istream & | operator>> (std::istream &a_in, safe_num< T > &a_class) |
| Arithmetic operator. | |
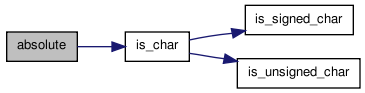
| T absolute | ( | const T & | a_num | ) | [inline] |
Return the absolute value of a numeric type.
Caveat: For some types, the maximum negative value is one larger than the maximum positive value: specifically char. Depending on the type and value, it may be impossible to return the absolute value. For such types under such circumstances an exception is thrown.
Definition at line 220 of file rmath.h.
References ERROR, INTERNAL_ERROR, is_char(), and TRY_nomem.
Referenced by safe_num< T >::add(), safe_num< T >::subtract(), test2(), and test7().
| static const T highest_value | ( | const T & | a_arg | ) | [inline, static] |
| static const T highest_value | ( | void | ) | [inline, static] |
Return the maximum possible value a type may hold.
This is just a convenience function to match lowest_value<T>(). All it does is return the value of max_limit<T>().
| static const T lowest_value | ( | const T & | a_arg | ) | [inline, static] |
| static const T lowest_value | ( | void | ) | [inline, static] |
| static const T max_limit | ( | const T & | a_arg | ) | [inline, static] |
| static const T max_limit | ( | ) | [inline, static] |
A small set of numeric limits routines, since gcc prior to 3.x doesn't have numeric_limits.
Find the maximum limit for a type, equivalent to std::numeric_limits<T>.max() for systems that don't have the limits c++ header file.
Definition at line 20 of file rmath.h.
Referenced by test3(), and vault_manager::usage().
| const double max_limit< double > | ( | ) | [inline] |
Return the largest possible number that a double may hold.
Referenced by test4().
| const float max_limit< float > | ( | ) | [inline] |
Return the largest possible number that a float may hold.
Referenced by test4().
| static const T min_limit | ( | const T & | a_arg | ) | [inline, static] |
| static const T min_limit | ( | ) | [inline, static] |
| const double min_limit< double > | ( | ) | [inline] |
Return the smallest positive number that a double may hold.
Caveat: This is in contrast to other types, where min_limit<T>() will return either 0 or the largest possible negative number that the type may hold. If you are looking for the largest possible negative number for any given type, use lowest_value<T>() instead.
Referenced by test4().
| const float min_limit< float > | ( | ) | [inline] |
Return the smallest positive number that a float may hold.
Caveat: This is in contrast to other types, where min_limit<T>() will return either 0 or the largest possible negative number that the type may hold. If you are looking for the largest possible negative number for any given type, use lowest_value<T>() instead.
Referenced by test4().
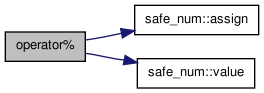
| safe_num<T> operator% | ( | safe_num< T > | a_class1, | |
| safe_num< T > | a_class2 | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Arithmetic operator.
Definition at line 725 of file rmath.h.
References safe_num< T >::assign(), and safe_num< T >::value().
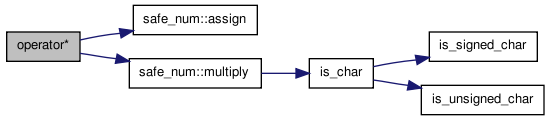
| safe_num<T> operator* | ( | safe_num< T > | a_class1, | |
| safe_num< T > | a_class2 | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Arithmetic operator.
Definition at line 701 of file rmath.h.
References safe_num< T >::assign(), and safe_num< T >::multiply().
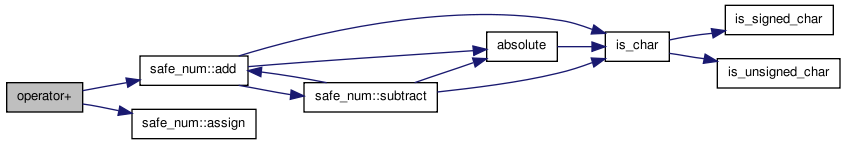
| safe_num<T> operator+ | ( | safe_num< T > | a_class1, | |
| safe_num< T > | a_class2 | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Arithmetic operator.
Definition at line 677 of file rmath.h.
References safe_num< T >::add(), and safe_num< T >::assign().
Arithmetic operator.
Definition at line 745 of file rmath.h.
References safe_num< T >::add(), and safe_num< T >::assign().
Arithmetic operator.
Definition at line 736 of file rmath.h.
References safe_num< T >::add().
| safe_num<T> operator- | ( | safe_num< T > | a_class1, | |
| safe_num< T > | a_class2 | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Arithmetic operator.
Definition at line 689 of file rmath.h.
References safe_num< T >::assign(), and safe_num< T >::subtract().
Arithmetic operator.
Definition at line 766 of file rmath.h.
References safe_num< T >::assign(), and safe_num< T >::subtract().
Arithmetic operator.
Definition at line 757 of file rmath.h.
References safe_num< T >::subtract().
| safe_num<T> operator/ | ( | safe_num< T > | a_class1, | |
| safe_num< T > | a_class2 | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Arithmetic operator.
Definition at line 713 of file rmath.h.
References safe_num< T >::assign(), and safe_num< T >::divide().
| std::ostream& operator<< | ( | std::ostream & | a_out, | |
| safe_num< T > | a_class | |||
| ) | [inline] |
 1.6.1
1.6.1